DRV8301DCAR motor drive chip cleaning inventory price is the lowest
characteristic
Voltage range of 6-V to 60V working power supply
1.7-A source and 2.3-A drain drive current capability
Conversion rate control for reducing EMI
100% duty cycle hoist door driver
support
6 - or 3-PWM input mode
Dual Integrated Current Shunt Amplifier
Adjustable gain and offset
Integrated 1.5-A buck converter
3.3V and 5-V interface support
SPI
Protection function:
Programmable dead time control (DTC)
Programmable overcurrent protection (OCP)
PVDD and GVDD undervoltage lockout
(UV)
GVDD overvoltage lockout (OVLO)
Overheating warning/shutdown
(OTW/OTS)
Reporting via nFAULT, nOCTW and SPI
register
explain
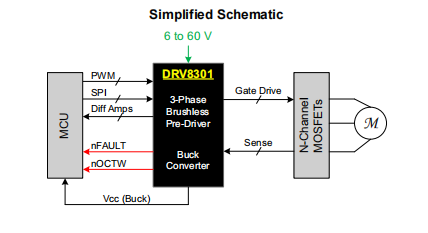
The DRV8301 is a grid driver IC for three-phase motor drive applications. The device provides three half bridge drivers, and each half bridge driver can drive two N-channel MOSFETs. The DRV8301 supports up to 1.7A power supply and 2.3A peak current capability. The DRV8301 can use a single power supply in a wide range of 6-V to 60V.
The device uses a bootstrap gate driver architecture with trickle charging circuit to support 100% duty cycle. When the high side or low side MOSFET switches to prevent current flow, DRV8301 uses automatic handshake. The integrated VDS sensing of the high side and low side MOSFETs is used to protect the external power stage from overcurrent conditions. The DRV8301 includes two current shunt amplifiers for accurate current measurement. The amplifier supports bi-directional current sensing and provides adjustable output offsets of up to 3V.
The DRV8301 also includes an integrated switch mode buck converter with adjustable output and switching frequency. The step-down converter can provide current up to 1.5A to support MCU or other system power requirements. SPI provides detailed fault reports and flexible parameter settings, such as gain options for current shunt amplifiers and conversion rate control for gate drivers.
application
• Three phase brushless DC motor and permanent magnet synchronous motor
• CPAP and pumps
• Electric bicycles
• Power tools
• Robots and RC toys
• Industrial automation
Voltage range of 6-V to 60V working power supply
1.7-A source and 2.3-A drain drive current capability
Conversion rate control for reducing EMI
100% duty cycle hoist door driver
support
6 - or 3-PWM input mode
Dual Integrated Current Shunt Amplifier
Adjustable gain and offset
Integrated 1.5-A buck converter
3.3V and 5-V interface support
SPI
Protection function:
Programmable dead time control (DTC)
Programmable overcurrent protection (OCP)
PVDD and GVDD undervoltage lockout
(UV)
GVDD overvoltage lockout (OVLO)
Overheating warning/shutdown
(OTW/OTS)
Reporting via nFAULT, nOCTW and SPI
register
explain
The DRV8301 is a grid driver IC for three-phase motor drive applications. The device provides three half bridge drivers, and each half bridge driver can drive two N-channel MOSFETs. The DRV8301 supports up to 1.7A power supply and 2.3A peak current capability. The DRV8301 can use a single power supply in a wide range of 6-V to 60V.
The device uses a bootstrap gate driver architecture with trickle charging circuit to support 100% duty cycle. When the high side or low side MOSFET switches to prevent current flow, DRV8301 uses automatic handshake. The integrated VDS sensing of the high side and low side MOSFETs is used to protect the external power stage from overcurrent conditions. The DRV8301 includes two current shunt amplifiers for accurate current measurement. The amplifier supports bi-directional current sensing and provides adjustable output offsets of up to 3V.
The DRV8301 also includes an integrated switch mode buck converter with adjustable output and switching frequency. The step-down converter can provide current up to 1.5A to support MCU or other system power requirements. SPI provides detailed fault reports and flexible parameter settings, such as gain options for current shunt amplifiers and conversion rate control for gate drivers.
application
• Three phase brushless DC motor and permanent magnet synchronous motor
• CPAP and pumps
• Electric bicycles
• Power tools
• Robots and RC toys
• Industrial automation
Schematic diagram